Sim racing has transformed from a niche gaming genre into a high-precision motorsport training tool and billion-dollar industry. Initially seen as entertainment, modern simulators now offer hyper-realistic physics, AI-driven opponents, and professional-grade racing analytics.
With its roots in the 1980s and rapid advancements in VR, AI, and esports, sim racing is revolutionizing both virtual and real-world motorsports. This article explores its evolution, technological advancements, real-world applications, and future potential—offering insight into why sim racing is more than just a game.
The Evolution of Sim Racing: From Arcade to Precision Engineering
1980s-1990s: Laying the Foundation
Early racing games like Revs (1984) introduced physics-based handling, while IndyCar Racing (1993) pioneered aerodynamic simulation and tire wear mechanics, setting sim racing apart from arcade games.
2000s: The Birth of Online Racing & Advanced Physics
Titles like iRacing and GTR 2 pushed realism further with laser-scanned tracks, dynamic weather, and online ranked competitions, bringing real-world racing strategy into virtual leagues.
2010s-Present: Esports, VR, and Real-World Crossover
Sim racing became an official training tool for professional teams. Formula 1, NASCAR, and endurance teams began using rFactor 2 and Assetto Corsa Competizione for track familiarization and race preparation. AI-driven opponents and machine learning analytics now allow racers to train against adaptive, real-world-calibrated simulations.
Key Insight: Sim racing has evolved from a hobby into a training ground for professional drivers, influencing motorsports strategy and talent scouting.
Sim Racing’s Influence on Professional Motorsports
Sim racing is now a critical tool for professional motorsport teams, providing high-precision, risk-free training environments.
Real-World Drivers Who Started as Sim Racers
1️⃣ Jann Mardenborough (Gran Turismo Academy → Professional GT Racer)
2️⃣ James Baldwin (World’s Fastest Gamer → McLaren Driver Development Program)
3️⃣ Max Verstappen & Lando Norris (F1 drivers who actively train with sim racing setups)
Why Professional Teams Use Sim Racing
✔ Track Memorization: Drivers can practice braking points, racing lines, and overtaking zones before race weekends.
✔ Telemetry & Data Analysis: Engineers use real-time data logging from simulators to test tire wear, fuel consumption, and aerodynamics.
✔ Cost-Effective Training: Simulators eliminate the need for physical track time, reducing budget constraints for junior drivers.
Research Insight: A 2022 study from the Journal of Sports Science & Medicine found that sim racers develop comparable reaction times and spatial awareness to real-world drivers, supporting sim racing’s effectiveness as a professional training tool.
The Hardware Behind Sim Racing: Immersion & Precision
Sim racing isn’t just about software—it’s powered by high-end, precision-engineered hardware that recreates real-world driving conditions.
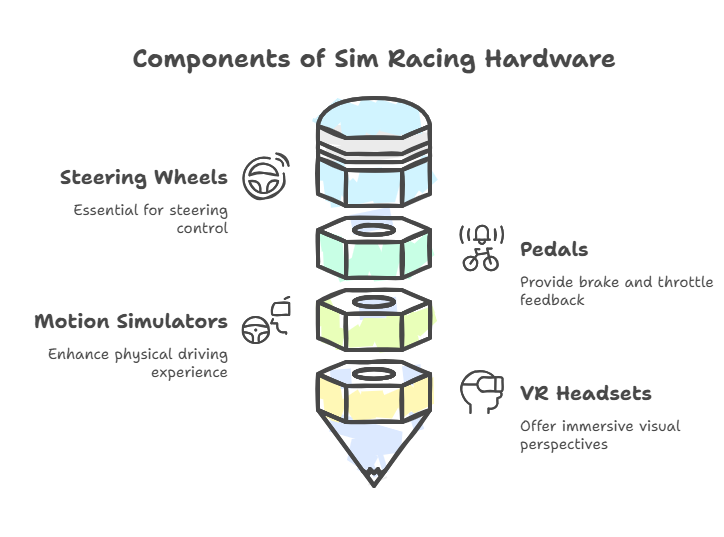
Essential Sim Racing Equipment
Force-Feedback Steering Wheels – Simulate road texture, oversteer, and tire grip loss.
Load-Cell Pedals – Provide real-world braking resistance, replicating F1 and GT car setups.
Triple-Screen & VR Setups – Increase depth perception and reaction times.
Motion Simulators – Replicate g-forces and elevation changes, mirroring cockpit movements in real racing.
Price Ranges:
- Entry-Level: $150-$500 (controller & basic wheel setup)
- Mid-Tier: $1,000-$5,000 (direct-drive wheelbase, professional pedals, VR headset)
- Pro-Level: $10,000+ (motion rigs, hydraulic force-feedback platforms, triple 4K screens)
Industry Trend: Top sim racers use high-end hardware that rivals real-world racing simulators used by F1 and Le Mans teams.
The Growing Role of AI and Machine Learning in Sim Racing
AI Opponents That Adapt in Real Time
Traditional AI follows pre-programmed racing lines, but new machine learning opponents can analyze human driving behavior and adapt in real time. This enables:
✔ Dynamic racing conditions based on driver aggression and weather changes.
✔ AI-generated telemetry analysis, offering customized coaching for racers.
✔ Predictive crash avoidance, mimicking human decision-making under pressure.
Key Future Trend: AI opponents could one day simulate individual racing styles, allowing players to race against virtual replicas of real-world F1 and endurance drivers.
Beyond Gaming: How Sim Racing is Shaping Industries
Sim racing isn’t just entertainment—it’s influencing multiple sectors, from cognitive research to automotive engineering.
1️⃣ Cognitive Training & Rehabilitation
A 2021 study in the International Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health found that sim racing enhances:
✔ Hand-eye coordination & reaction times
✔ Cognitive adaptability & strategic thinking
✔ Fine motor skills in older adults (potential applications in stroke recovery)
2️⃣ Automotive Industry & Data-Driven Insights
Automakers like Porsche, Ferrari, and McLaren use simulated vehicle testing to:
✔ Analyze aerodynamics & tire performance in real time.
✔ Gather driver behavior data for predictive safety systems.
✔ Develop AI-powered driver assistance based on esports telemetry.
3️⃣ The Rise of Esports & Sim Racing Careers
✔ The F1 Esports Series & Le Mans Virtual Series offer million-dollar prize pools.
✔ Sim racing scholarships are emerging, allowing talent to transition into real motorsports.
Key Future Trend: As VR, AI, and blockchain evolve, sim racing could become the leading talent discovery platform for real-world racing teams.
The Future of Sim Racing: What’s Next?
VR & Eye-Tracking Integration:
- Foveated rendering (focus-based VR rendering) will enable near-photorealistic cockpit views.
- Eye-tracking AI assistants could offer real-time coaching on racing lines & braking points.
Web3 & Blockchain-Powered Sim Racing
- NFT-backed race cars allow players to own & trade digital vehicles.
- Decentralized esports leagues, where race teams are funded by community governance tokens.
Autonomous Racing AI vs. Humans
- AI-powered racecars could compete against human drivers in esports tournaments.
- Hybrid AI-human endurance teams (AI handling strategy, humans executing the race).
Industry Insight: In the next decade, sim racing could evolve into an entirely new form of competitive motorsport, blending AI, esports, and professional racing.
Final Takeaways: Why Sim Racing is the Future of Motorsport
✅ Bridges esports & real-world racing, producing professional drivers & engineers.
✅ AI & machine learning are transforming how drivers train & compete.
✅ Beyond gaming, sim racing influences automotive research, cognitive training, and professional motorsport strategy.
✅ Future advancements in VR, AI, and blockchain could redefine racing & talent discovery.
Final Thought: Sim racing isn’t just a game—it’s a revolution in how we train, compete, and push the boundaries of motorsport innovation.
